This is the second in a four-part weekly series that examines RF Code's Edge Computing model. The goal of this series is to provide a foundational understanding of the core Edge requirements, the Edge objective values, product relevance and positioning, and how companies can evaluate and assess their path to Edge.
In part 1 of this series we examined the common attributes of Edge-oriented products. These are the baseline features or attributes that a product must exhibit in order to logically be considered an Edge product at all. The week we will look at the ways in which Edge -oriented products can be differentiated by building on their common attributes while addressing specific issues created by the implementation and delivery of an Edge Computing environment.
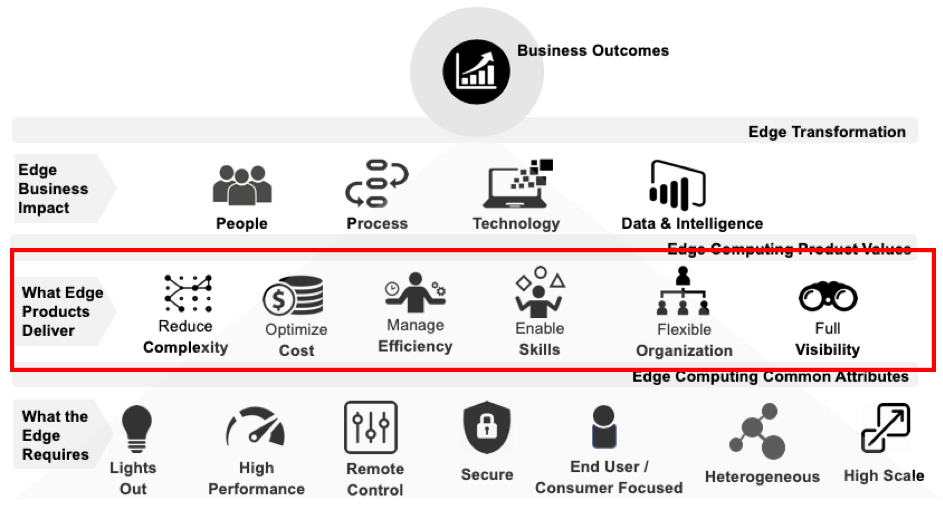 Figure 1. Layer 2 of the Edge Model: What Edge Products Deliver
Figure 1. Layer 2 of the Edge Model: What Edge Products Deliver
While the potential benefits of Edge deployments are many, delivering Edge also creates complexity, cost, efficiency, skills, organization and visibility challenges. Traditional data center approaches and technology will not solve the demands of Edge management: solving these problems requires the adoption of technologies that both deliver Edge and address the challenge areas it presents.
|
Example Edge Sizing (based on client feedback) |
|
|
• Tech Closet Network • Standalone Servers • Base 1-3 Racks |
• Small 4-10 Racks • Medium 11-25 Racks • Large 26+ Racks |
Reduce Complexity
An Edge product must reduce the complexity of managing large numbers of distributed systems.
Edge delivered at scale requires the same management as a corporate data center. Because each Edge environment may have a smaller footprint than a data center it does not necessarily mean lower complexity as it may contain networks, servers, storage, racks and power and cooling. Edge managed in its entirety can be far more complex than the largest of datacenters.
Edge Complexity Challenges
- Multiple points of reference to understand environmental conditions and impact on Edge assets
- Disparate monitoring points requiring greater cross team collaboration
- Disparate technology supporting different parts of the Edge creates high process complexity
- Assets tracking and environment monitoring requiring power and the network
- Infrastructure and environment require multiple monitors
- Customization required to integrate with Edge Assets or environmental systems
- No common source of truth
- No ability to compare infrastructure state and environmental performance across Edge facilities
Edge Complexity Summary
- Highly distributed with increasing numbers of remote locations requiring the same IT management capabilities as a corporate data center but accomplished at scale
- Edge environment size does not lower complexity requiring solutions that simplify how the Edge is controlled, changed, monitored and viewed
Optimize Cost
Edge plays a critical role in supporting a business that has focused on moving the IT data center infrastructure (or parts of the infrastructure) to the cloud. The Edge cannot be moved to the cloud and even with 5G it will need the compute resource near the consumer. The challenge is; Edge is not just another data center and if managed using the same diversity of skills, methods and technology per Edge location it creates significant cost. To manage cost requires an approach where Edge is managed holistically providing economies of scale, viewing the overall health of the hardware and environment across and within each Edge location to optimize skills and resources.
Edge Cost Challenges
- Different teams use different monitors to understand Edge health requiring more skilled personnel
- Edge location access and change is not monitored or guided, taking more time with greater risk
- Error reporting is a long process impacting business availability
- Asset tracking, when not connected to the network is a manual process
- Assets tracked using adapters, custom integration and additional skills
- Multiple skills and personnel required to monitor the Edge infrastructure
- Environment health checked using multiple monitors and system consoles
- No consolidated power and energy comparisons to allow changes to optimize consumption
- Edge rack capacity not monitored to enable resource optimization
- Manual asset movement tracking resulting in lost or mislaid assets
Edge Cost Summary
- Monitor Edge state aligned to business impact
- Holistic management solutions provide economies of scale, while optimizing skills and resources
- Simplify and automate processes for change, monitoring, remediation and reporting
Manage Efficiency
Edge inefficiency spans many areas including an inability to understand Edge conditions, slow issue remediation, poor change controls, no remote visualization, a lack of physical security access control, uncoordinated support resources, uncollaborative siloed responsibilities, not enough skills, too many tools or the wrong tools. These inefficiencies are a result of traditional data center thinking and using technology that cannot adapt and manage the highly distributed Edge environment.
Edge Efficiency Challenges
- Silo’s create monitoring inefficiencies, conflict and ‘true state' disparity
- Specialists required to interpret different Edge systems
- Large teams required to manage Edge locations and the heterogeneous equipment
- Physical passive asset tagging is a manual process
- Multiple monitors required to understand Edge state
- Edge issues are not aligned with the impact on the business
- Network performance at the Edge impacts infrastructure monitoring
- No integration with DCIM, environment and service mgmt. products creates inefficiencies in problem management and resolution
- No information to compare the environmental efficiency across all Edge locations
- No consolidated data to compare the efficiency of different power and cooling systems
Edge Efficiency Summary
- Deliver efficiencies for Edge state and performance monitoring, issue remediation, change control, organizational collaboration, skills optimization and enablement
- Solutions provide a measurable path of efficiency improvement
Enable Skills
Expensive, highly skilled, personnel are required to effectively manage the disparate complexities of a data center. Each area within a data center has resources focused on their own management function (network, servers, storage, power & cooling etc.). The number of components in each area can be substantial and therefore creating a management silo with little understanding of adjacent areas. The same skills are required to manage the Edge; however, the amount of technology is less requiring lower skills to manage each areas capacity with higher skills to understand how each Edge area supports and impacts others.
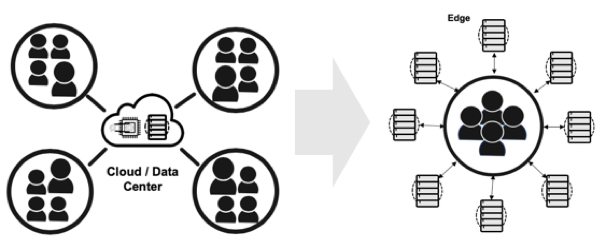
Figure 3: Data Center Organization & Skills > Edge Organization & Skills
Edge Skills Challenges
- Silo’s create monitoring inefficiencies, conflict and ‘true state' disparity
- Specialists required to interpret different Edge systems
- Large teams required to manage Edge locations and the heterogeneous equipment
- Physical passive asset tagging is a manual process
- Multiple monitors required to understand Edge state
- Edge issues are not aligned with the impact on the business
- Network performance at the Edge impacts infrastructure monitoring
- No integration with DCIM, environment and service mgmt. products create inefficiencies in problem management and resolution
- No information to compare the environmental efficiency across all Edge locations
- No consolidated data to compare the efficiency of different power and cooling systems
As companies move to Edge, management technology is needed that both monitors each Edge component, correlates state and shows holistically the overall health of Edge, providing information that is coherent, relevant and actionable to a broad number of skills.
Edge Skills Summary
- Reduce the need for expensive, highly skilled, personnel required to manage the complexities of an Edge data center environment
- Remove management silos created as each technology area becomes a domain requiring its own expertise
- Meet the needs of the domain expert and provide capabilities and information to other support personnel
- Enable personnel without deep technical knowledge to understand issues and provide them with actionable information
Flexible Organization
Edge implementations vary in size, complexity, environment and business model therefore, the personnel responsible for managing and supporting the Edge also varies. This demands technology that provides a single source of truth, providing right information to a broad number of people and roles using easy to understand roles-based views.
Edge Organization Challenges
- Management silos create organizational and process complexity demanding high levels of collaborative maturity
- Each team chooses their own management tools creating organizational barriers and inhibiting collaboration
- Each team uses their own tools and monitors creating a fragmented view on the health and state of the Edge infrastructure.
- Problems take longer to identify and solve
- Each team uses their own tools and monitors creating a fragmented, unintegrated data and conflicting information
- Personnel use interfaces and monitors that do not provide information specific to their role
Edge Organization Summary
- Provide management capabilities with holistic capabilities that can be used by the domain experts and other management teams
- Solutions must eliminate data center organizational barriers allowing each team to choose their own Edge views and functions
Full Visibility
Each Edge location requires physical changes and maintenance. These activities need to be guided to ensure the no mistakes are made. This requires remotely enabled visibility into Edge locations that software, video and phone support alone cannot provide. In addition, the definition of ‘Edge’ must include ALL Edge components. Without this capability things like Edge security (physical and digital) and compliance (e.g. change) cannot be accomplished.
Edge Visibility Challenges
- A large group of people from different teams required to monitor the Edge infrastructure
- Assets lifecycle tracked manually
- No understanding of how the environment impacts the Edge rack assets
- ‘Edge infrastructure change and maintenance carried out without guidance
- Fragmented view of the Edge infrastructure
- No integrated video
- No consolidated cross Edge location environmental data
- Multiple monitors and dashboards
Edge Visibility Summary
- ‘Lights Out’ Edge locations require advanced capabilities to understand the full state of the environment, which includes the entire Edge infrastructure, facility access, and activity monitoring
- Edge solutions provide security (physical and digital), compliance (e.g. change) and remote guided maintenance and support cannot be accomplished
As can be seen, the challenges introduced by Edge deployments are many, but they also present ample opportunities for organizations to select new technologies specifically designed to address those very challenges head on. In Part 3 of this series we examine the ways in which businesses can best achieve business value from Edge technology.




