
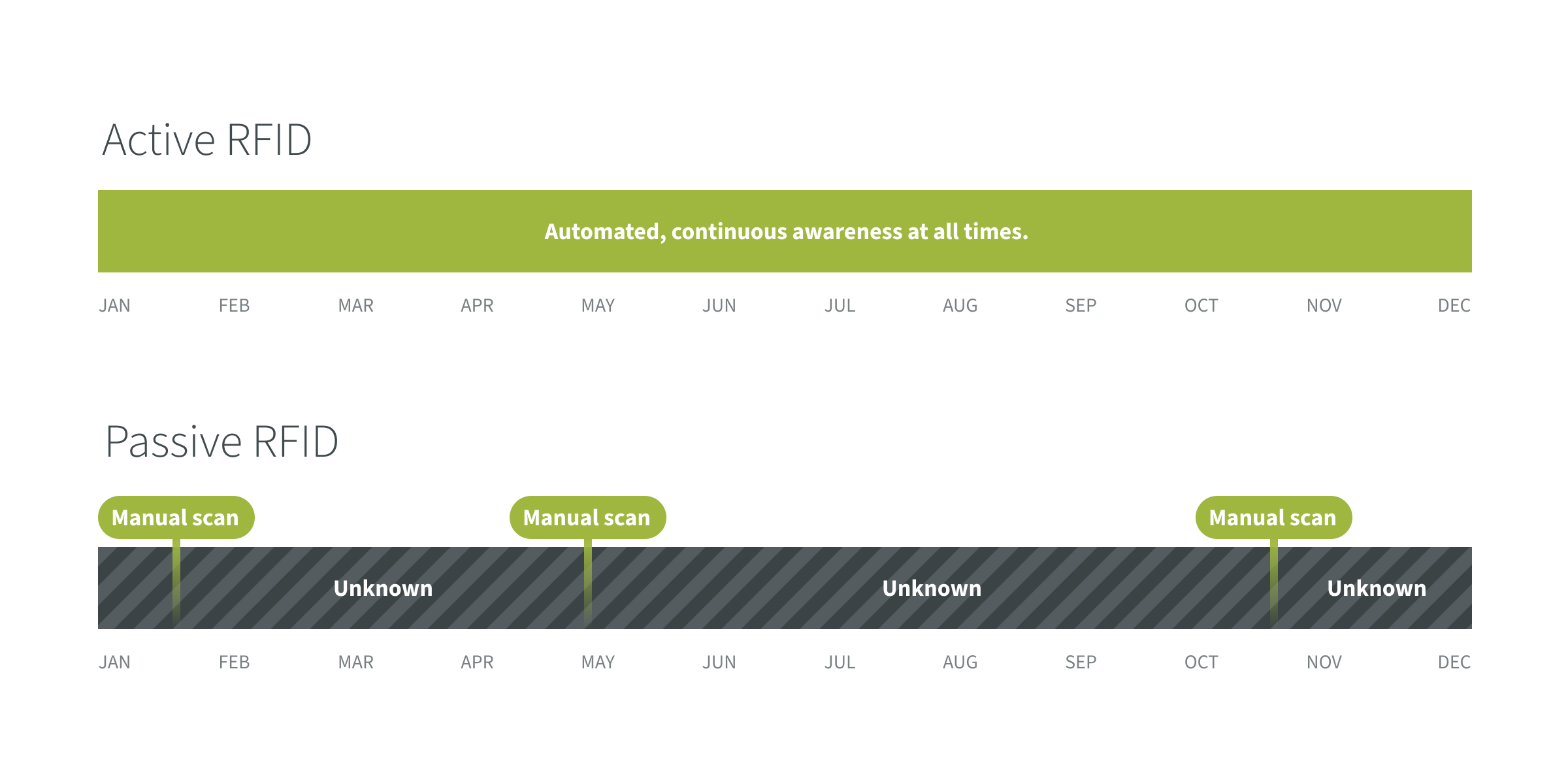
Active and passive RFID asset tracking operate very differently.
An active RFID asset tag actively sends a signal and uses an internal power source to operate continually without human intervention. A passive tag does not.
A passive tag needs to be activated manually so it can be read. To read a passive tag a person needs to be close to the passive tag with a passive tag reader. At all other times the tag is inactive and not being read.
| Active | Passive | Barcode | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Actively sends a signal |
|
✖️ |
✖️ |
|
Internal power source |
|
✖️ |
✖️ |
|
Operates automatically |
|
✖️ |
✖️ |
|
Age of location data |
+/- 2 minutes |
Last manual scan |
Last manual scan |
|
Asset tag read volume |
1,400 per reader, simultaneously |
One asset tag at a time per person |
One asset tag at a time per person |
|
Asset tag read frequency |
Continuous, automatic |
One time, manual |
One time, manual |
|
Read distance |
Up to 300 feet (91m) |
Close to the tag (3 – 12 inches) |
Close to the tag (3 – 12 inches) |
Active RFID for data center asset management can eliminate manual effort whereas passive RFID can augment manual effort.
Active RFID
Active RFID asset tags can replace manual audit effort.
Audits happen continuously and automatically. With active RFID the detected location is compared against the asset’s recorded location and mismatches are reported. Customers have replaced manual asset audits with active RFID tags. Saving time and money.
Passive RFID
Passive RFID asset tags support manual audit effort.
There is no getting around it, even with passive RFID you need to send a team to find and count assets inside your own data centers. Passive RFID may provide some efficiency and productivity improvements when compared to using other manual approaches like spreadsheets.
Active RFID
Active RFID asset tags can provide real time inventory reporting and reduce the cost of assets at rest.
Continuously and automatically detects all assets in all locations by rack, room and zone and includes assets that aren’t connected to the network. Active RFID asset tags will tell you where each asset is now (which can prevent hundreds of wasted hours searching for assets). Based on rack, room or zone location active RFID can tell you the current lifecycle status of all assets. Customers love when assets arrive on the loading dock and are detected automatically.
Passive RFID
Passive RFID asset tags can provide “last scanned” inventory reporting.
Provides a snapshot of the last time assets were scanned, but doesn’t tell you the current state of the entire asset inventory in real time. For locating assets in storage or misplaced assets passive can tell you the last scanned location, but not where the asset is currently located. Passive RFID may provide some efficiency and productivity improvements when compared to using other manual approaches like spreadsheets.
Active RFID
Active RFID asset tracking solutions can replace manual effort entirely.
Data centers define the modern technology era, but data center teams still track and locate assets and maintain asset records manually. Active RFID replaces that manual effort. Need to locate an available asset? Look up its location in real time and go to where it is now, not where it was last scanned. Perform asset audits and reconciliation manually? Perform continuous audits automatically instead. Data center teams can do more with the resources they have.
Passive RFID
Passive RFID asset tracking solutions can reduce some record keeping effort.
Passive RFID augments manual process. Which can provide some productivity improvements. Reading a passive RFID tag is more convenient than dragging around a laptop and manually performing a search in an asset management system. The process may be only slightly better than scanning a barcode or QR code. Passive RFID tags get their power from the passive tag reader – the first step in reading a passive tag is powering and waking the tag with the passive reader.
Active RFID
Active RFID asset tracking solutions can have high impact on compliance and can reduce the costs associated with loss.
Active RFID automatically and continually maintains an asset chain of custody and can alert to bring attention to problems. The time, date and location of each asset is automatically recorded for the life of the asset – from the time it is received to the time it is disposed. Active RFID asset tags are also used on hard drives that have been removed awaiting disposal to minimize the risk of data exposure and avoid millions of dollars in fines and lawsuits. The number of lost or stolen assets can be reduced and the time spent trying to find assets can be eliminated.
Passive RFID
Passive RFID asset tracking solutions struggle to meaningfully impact compliance and loss.
Passive RFID can augment manual effort, without eliminating the largest contributors to manual effort. In some cases, passive RFID may not provide a return that is better than barcode or QR code scanning solutions. These solutions all share the need to continue to manually perform asset tracking, asset audits and asset inventory, and at best can tell you where assets were the last time they were read or scanned.
Active RFID
Active RFID asset tracking solutions provide a greater cumulative return.
Because of their active technology active RFID tags may have a higher price per tag than a passive tag. The possible return on investment from active RFID is higher because of the ability to enable data center teams to eliminate manual audit effort (or cancel outsourced audit services), reduce the cost of capital at rest through optimized inventory, boost data center team productivity to do more with the resources they have, and can significantly reduce the impacts of non-compliance and loss.
Passive RFID
Passive RFID tags have a lower price than active RFID tags, and a lower return.
Passive RFID can augment manual effort, without eliminating the largest contributors to manual effort. In some cases, passive RFID may not provide a return that is better than barcode or QR code scanning solutions. These solutions all share the need to continue to manually perform asset tracking, asset audits and asset inventory, and at best can tell you where assets were the last time they were read or scanned.
Learn from the experience of others with interviews and other resources.